T-Series: Guitar Build Guide
by Richard Norton 17/12/2025
Welcome to the Guitar Anatomy T-Series Build Guide. This is a detailed walk through for building a Tele-style guitar using professional-quality parts. This tutorial is designed to help you assemble one of our Guitar Anatomy T-Series DIY kits, which include all required hardware, electronics and adjustment tools. Whether you’re building a Tele-style guitar, creating a custom partscaster or upgrading an existing Telecaster, this guide covers the full process from assembly to setup.
The instructions apply to all Telecaster-style and Tele-compatible builds, even if you are combining parts from different manufacturers.
This guide focuses on assembly, wiring and setup, with no woodworking required (for example, carving your own body and neck).
If you are building a Stratocaster or Strat-style guitar, please see our dedicated Stratocaster Build Guide.
Tools Required
Essential Tools
- Phillips screwdrivers: PH0, PH1, PH2
- Drill and bits: 1.5 mm, 2 mm, 3 mm and 10 mm (for 2-point trem)
- 11 mm & 12mm spanner or socket
- Soldering iron & solder
- Ruler or tape measure
- Masking tape
- Pencil / bradawl
- Wire strippers
- Sandpaper (various, for small fit adjustments) – see our dedicated setup guide
Optional
- String winder
- Heat shrink tubing
- Cable ties
- Multimeter
- Small pliers / tweezers
- Rubber mallet
Setup Tools
- Nut files
- Tuner
- Feeler gauges
- All required Allen keys (included with GA kits)
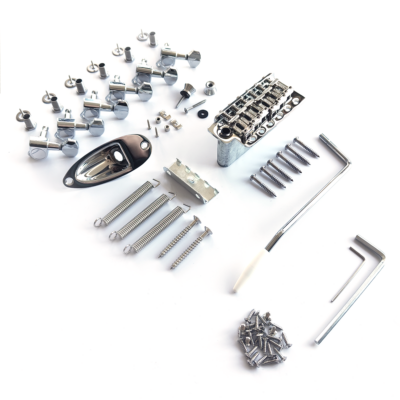
Parts Checklist
(If using a Guitar Anatomy kit, all parts are included.)
Major Components
• Telecaster body (standard routing)
• Neck
Hardware
• Tele bridge with 3 saddle or 6 saddle design
• Ferrules (string through body)
• Neck plate and screws
• Pickguard
• Control plate
• Tuners (6 inline)
• String tree (s)
• Strap buttons and screws
• Jack cup or electrosocket jack plate
Electronics
• GA wiring kit (pots, switch, wire, cap)
• Neck pickup
• Bridge pickup
• Knobs
• Solder and wire
Fittings
• Pickguard screws (8)
• Control plate screws (2)
• Bridge screws (4-6, depending on bridge)
• Ferrules (6)
• Tuner screws (6)
• String tree screw (1)
Shaping the Headstock (All GA Kits)
All Guitar Anatomy build kits come with an unshaped half-paddle headstock, giving you the freedom to create your own design. In this guide we will not cover the full cutting and shaping process, but shaping a headstock is much easier than most beginners expect.
Before cutting your headstock, we strongly recommend doing a quick dry fit of your neck, body, tuners and bridge. This ensures everything lines up correctly before you commit to your final headstock outline.
Once you’re ready to shape your design, here are some resources we recommend for clear guidance:
- Long-time collaborator Michael Largerstedt guides you through shaping and cutting your own design from a GA neck.
- Long-time collaborator MixwithABD guides you through shaping and cutting your own design from a GA neck.
Take your time when marking and cutting, and sand the edges smooth before continuing with assembly. Once shaped, the rest of this build guide applies exactly the same as normal.
If you would like further advice on this step, get in touch with the GA team.
STEP 1 — BEFORE YOU BEGIN
Prepare Workspace
- Use a stable, well-lit bench
- Lay down a soft cloth or pad to protect your components
- Organise tools and small parts
Dry Fit Check
Before drilling or soldering:
- Ensure the neck fits snugly into the pocket
- Check bridge rout and control plate position (Figure 1A)
- Confirm the 25.5 inch scale length (nut → saddles ≈ 25.5″). (Figure 1B)
*Scale length is the vibrating length of the string measured from the nut to where it meets the saddle. Frets are spaced according to this distance, so the bridge must sit in the correct position for proper intonation.
💡 Tip: Small bowls help prevent losing screws.
Figure 1A
Figure 1B
You’re ready to begin.
STEP 2 — NECK & HARDWARE PREPARATION
A. Fit the Tuners
- Insert each tuner from the back of the headstock (Figure 2A)
- Add washer + threaded bushing from the front; finger-tight.
- Align tuners using a ruler (Figure 2B).
- Mark locator screw holes.
- Remove tuners, drill 1.5 mm pilot holes (to the depth of the screw).
💡 Tip: Add masking tape around the drill bit to act as a depth guide so you drill the right depth.
- Refit tuners and tighten bushings with a spanner or socket.
- Install locator screws.
Figure 2A
Figure 2B
Figure 2C
B. Fit the Strap Buttons
-
- Position buttons: Lower bout and Upper horn
- Mark holes.
- Drill 1.5 mm × 6–8 mm.
- Fit button + felt washer (Figure 2D & 2E)
- Tighten screws snugly.
Figure 2D
Figure 2E
C. Neck, Body & Bridge Alignment
-
- Seat the neck in the pocket. (Figure 2F)
*Note: Some Telecaster necks have 21 frets, others have 22. A 22 fret neck has a small fretboard overhang. A 21 fret neck stops at the heel. Both fit the same neck pocket.
- Place the Tele bridge roughly in position.
- Fit low E and high e strings loosely (Figure 2H). (You can also use twine).
- Ensure strings run evenly along both fretboard edges (Figure 2J)
- Check scale length: (Figure 2H)
12th fret → saddle ≈ 75″ (324 mm) (Remember, you do have some adjustment in your saddles, so don’t expect it to be exact) - Adjust neck position until there is an even gap between the outer strings and the fretboard edges. *This prevents strings slipping off the edge during playing and ensures consistent feel across the neck.
- Once aligned, mark the bridge position
💡 Tip: Add masking tape around the neck joint to hold the neck firmly in place while you mark the bridge location.

Figure 2F

Figure 2G
Figure 2H
D. Drill Bridge Mounting Holes
Now we have our alignment, we will secure the bridge. Remove the strings from the neck & bridge and keep them to one side.
- Mark bridge screw holes
• Drill 2 mm x 12 to 14 mm deep
• Keep drill vertical
*Modern Tele Bridge Note
Modern Tele bridges use a different footprint. Guitar Anatomy Tele bodies do not accept modern Tele bridges without modification. Contact the GA team for advice.
STEP 3 – BRIDGE INSTALLATION
A. Fit Bridge Pickup and Route Wires
The Tele bridge pickup mounts underneath the bridge plate and must be installed first.
- Fit the bridge pickup into the bridge plate. Fit pickups from back; mount with screws + springs. (Figure 3A & 3B)
- Route the pickup wires through the body into the control cavity (Figure 3C)
- Leave enough slack so wires are not tight
Figure 3A
Figure 3B
Figure 3C
B. Fit the Bridge Plate
- Position bridge over pilot holes (Figure 3A)
- Ensure pickup wires are not trapped
- Tighten screws evenly so the bridge sits flat (Figure 3D)
Figure 3D
C. Fit the Ferrules ( Figure 3D & 3F)
(If not pre-installed)
- Insert ferrules into the back of the body
- Press in by hand or tap gently with a rubber mallet
- Ensure ferrules sit flush
Note* If ferrules feel slightly loose, this is normal. String tension will pull them securely into place. A small amount of wood glue can be used if desired. Avoid superglue.
Figure 3E
Figure 3F
OPTIONAL — SHIELDING
- Shielding is optional, but highly recommended. It helps reduce electrical hum, especially with single-coil pickups—and usually results in a cleaner, quieter guitar. It adds a few minutes to the build, but the improvement is worth it.
-
Materials
- Copper foil tape or shielding paint.
-
Method
- Line cavities with overlapping foil, or paint 2–3 coats.
- Shield underside of pickguard.
- Ensure body and pickguard shielding make contact.
- Use multimeter to confirm continuity (Optional)
Figure 3G
STEP 4 — FIT PICKUPS AND PICKGUARD
A.Fit the Neck Pickup to the Pickguard
On Guitar Anatomy kits, the Tele neck pickup mounts directly to the pickguard.
- Insert the pickup into the pickguard cut-out from the rear (Figure 4A)
• Place the pickup springs between the pickup and the underside of the pickguard (Figure 4B)
• Thread each mounting screw through the pickguard, through the spring, and into the pickup
Note* The purpose of the springs is to allow pickup height adjustment later by turning the mounting screws.
Some pickups use rubber tubing instead of springs. This works on the same principle, providing tension so the pickup height can be adjusted.
Note: On some non-GA builds, the Tele neck pickup may mount directly to the body instead of the pickguard. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions if this applies.
Figure 4A
Figure 4B
- Route the neck pickup wires through to the control cavity (Figure 4C)
- Leave enough slack for adjustment
Figure 4C
B. Fit the Pickguard
- Position and align the pickguard. (Figure 4A)
- Mark the screw hole locations.
Tip: You can either hold the pickguard by hand or use masking tape to keep it in place while marking. - Drill pilot holes using a 1.5 mm bit, around 6–8 mm deep.
- Install the pickguard – For now, just add 2 screws to secure in place. This is just in case you need to access the pickup again. The remaining screws can be added later.
STEP 5 — INSTALLING THE OUTPUT JACK
A. Assemble and Solder Jack
NOTE* If you are not experienced with soldering, please read the following soldering basics before attempting to solder.
• Fit the jack into the electro socket cup
• Tighten the nut with a 12 mm spanner or socket
• Solder wires to the jack (Figure 5A)
– Hot to inner lug
– Ground to outer lug
• Allow joints to cool naturally
Figure 5A
Soldering Basics
Before starting:
- Work in a well-ventilated space.
- Wear eye protection and keep the iron in a stand.
- Remember: the tip is extremely hot and stays hot after turning off (even when powered off).
How to Make a Good Joint
- Heat the part (lug/tab), not the solder.
Let the metal get hot first. - Feed solder once warm.
It should flow smoothly onto the surface. - Let it cool naturally.
Don’t move the wire until the solder sets.
💡 Tip: Good joints look smooth and shiny, not dull or cracked.
Grounding to Pot Casing
- Lightly scratch the casing to remove coating.
- Tin the pot and tin the wire
- Bring them together and heat for 2–3 seconds so the solder melts together.
⚠ Avoid prolonged heating. Too much heat can damage the pot internally.
Tidy Wiring (Optional)
- Use heat-shrink tubing over exposed joins.
- Keep wires neat with ties or small clips.
- Leave slight slack to prevent strain.
Safety Reminders
✔ Ventilate—avoid breathing fumes directly
✔ Wear eye protection
✔ Keep hot tools away from cables and surfaces
✔ Wash hands after soldering
B. Fit Electrosocket
- Install the assembled jack into the body
- Secure with screws
- Route jack wires through to the control cavity
At this stage, both pickups and the output jack should terminate in the control cavity.
Figure 5B
STEP 6 — CONTROL PLATE ASSEMBLY AND FINAL WIRING
A. Pre-Assemble the Control Plate
• Install volume and tone pots into the control plate
• Install the selector switch
• Tighten pot nuts with an 11 mm spanner or socket
• Ensure smooth operation
• Push fit knobs and switch tip
Pot Compatibility Note*
CTS pots are imperial sized. Alpha and many others are metric. Knobs must match the pot spline. All Guitar Anatomy kits include fully compatible components.
B. Final Wiring and Soldering
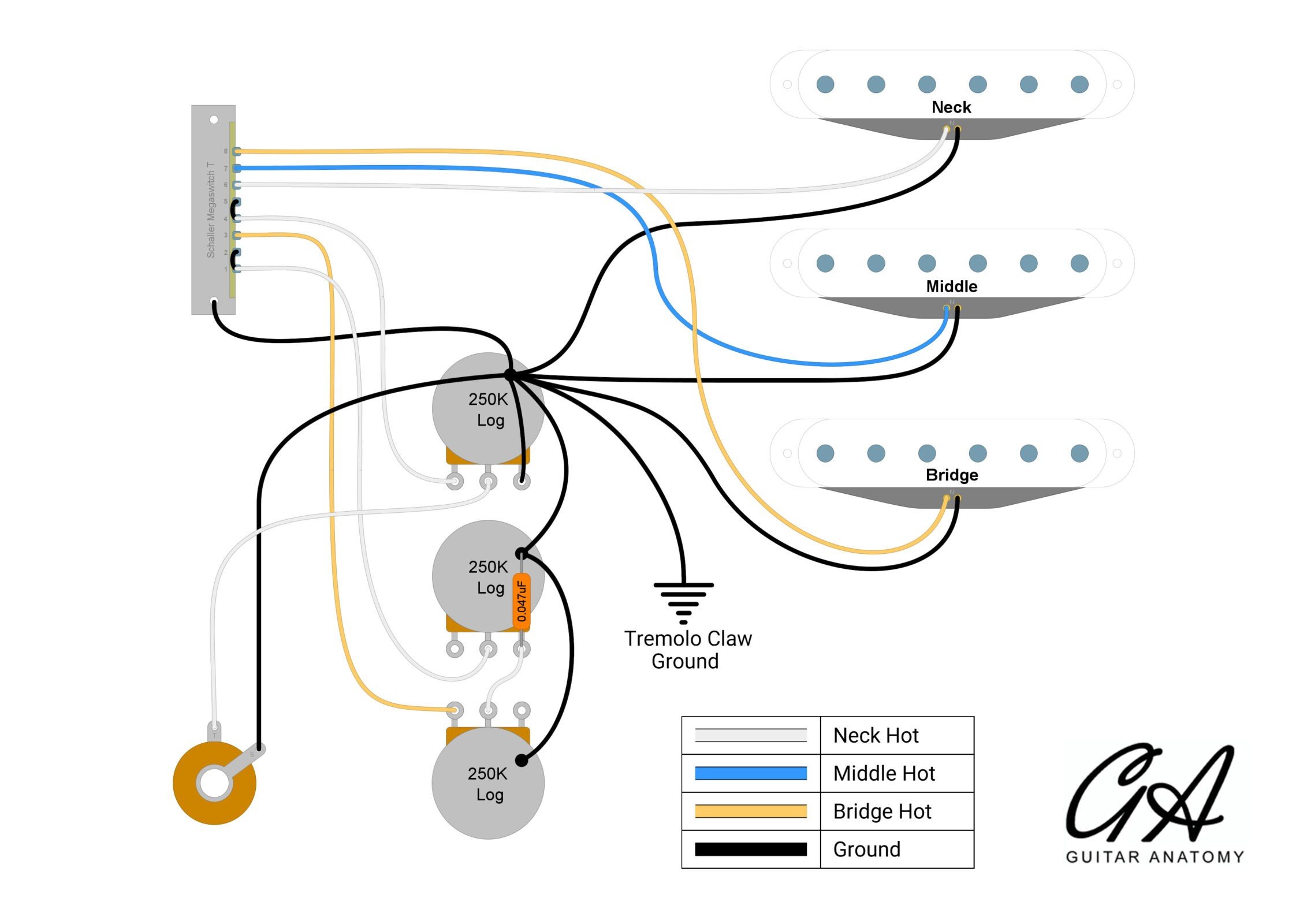
• Follow your Guitar Anatomy wiring diagram. Below shows our Standard Tele Wiring diagram. You can also find all of our diagrams HERE
• Follow all soldering, grounding and safety guidance
Figure 6A
Function Check
- Plug in a guitar cable—it should click in firmly and feel secure.
- Connect to an amp.
- Gently tap the pickup pole pieces (the small round metal dots on top of each pickup) with a screwdriver.
- You should hear a clear tapping sound for whichever pickup is selected.
- Switch pickup positions and repeat—each pickup should respond.
- Touch the bridge or strings; a slight hum should reduce—this shows the ground connection is good.
If it’s not working:
- No sound at all → check that both wires are soldered correctly to the jack lugs.
- Only noise or crackling → reflow the solder joints.
- One pickup works but another doesn’t → check wiring to the selector switch.
- No change when you touch metal parts → the ground wire may not be connected properly.
C. Install the Control Plate
- Tuck wires neatly into the cavity
• Screw the control plate to the body
• Do not overtighten👉 If the body is painted, drill 1.5 mm pilot holes first.
STEP 7 — Fitting The PICKGUARD
A. Check Fit
- Ensure pocket is clean
- Seat neck snugly
B. Align the Neck
- Fit low E and high e strings lightly (Figure 7A & 7B)
- Adjust until spacing along fretboard edges is even (Figure 7C)
Figure 7A
Figure 7B
Figure 7C
C. Mark & Drill Pilot Holes
- With neck in place, mark screw holes (make an indentation) through the body clearance holes. (You can use the neck screws for this, a pencil, or bradawl (Figure 7D)
- Remove neck.
- Insert a neck screw through the body with neck plate installed.
- Measure screw protrusion — this is your drill depth.
- Mark drill bit with masking tape.
- Drill 3 mm pilot holes to measured screw depth.
- Clean debris.
Figure 7D
D. Attach the Neck
- Position neck plate + (gasket) (Optional)
- Tighten screws in cross-pattern; firm, not overtight (Figure 7E)
💡 Tip: Don’t fully tighten one screw before starting the others.
Figure 7E
E. Final Check
- Confirm outer strings still align correctly.
- Adjust if needed.
STEP 8 — FIT PICKGUARD (FINAL)
- Secure pickguard fully
- Tele pickguards use 8 screws
- Tighten evenly
STEP 9 – STRING THE GUITAR AND INSTALL STRING TREE
A. String the Guitar
- Feed each string from the bridge up to the correct tuner post.
• Wind the strings so they wrap neatly downward on the post (2–3 turns for thin strings, 1–2 for thick ones).
• Tune to pitch.
• Gently stretch each string and re-tune.
💡 Once stretched and re-tuned, the guitar will hold tuning better.
B. Install String Tree (Figure 8A)
- With the strings now fitted and under light tension, position the string tree so it gives the correct downward pressure on the top two strings. Note* This is often in line with the A string tuner post, or thereabouts
• Mark the screw location and drill a small 1.5 mm pilot hole.
• Fit the string tree and tighten gently so it sits flat.
💡 Installing the string tree after stringing lets you use the actual string lines to place it accurately and avoid pulling the strings sideways.
Figure 9A
COMPLETED BUILD
Your Telecaster is now assembled, wired and playable. At this stage your guitar is fully assembled, but the action and playing feel will depend on your setup. You can now adjust string height, intonation and pickup height to suit your preference. If you are unsure, you can either take your guitar to a local luthier for a professional setup, or follow our full setup guides HERE, which walk you through every step including action targets, truss rod adjustments, and intonation settings.